Here is an updated online version of the 2013 white paper, “Flare Gas Measurement Using Thermal Mass Flow Meters,” by Bob Steinberg.
The reader can also access the original paper here.
Introduction
Flare and vent gas systems are used worldwide in various industries, including oil and gas production, refining, chemical processing, gas plants, wastewater treatment facilities, and landfills. The systems burn off waste gases, dispose of surplus gases, and protect people, equipment, and the environment. Flare gas measurement and monitoring are necessary to ensure that the flare system operates correctly. Additionally, strict environmental regulations often require the measurement of gas emitted into the atmosphere. Unfortunately, one must overcome the inherent challenges of measuring and monitoring flare gas, including extreme flow variation, the potential for changing the gas composition and working in hazardous locations. Thermal mass flow meters offer flare gas measurement and monitoring solutions in many applications.
What is Flare Gas?
Flare systems are commonly used in industrial plants worldwide. Flare gas is the surplus gas or vapor typically burned through a gas flare, also known as a flare stack. Gas flaring or venting is the process of burning off a combustible gas. A gas flare is a gas combustion device that burns off excess hydrocarbons that cannot be processed. This practice is a safety measure. If the gases were not burned and released into the atmosphere, it could create an explosive condition.

Before society accepted that global warming was an issue, gas flaring became a widely accepted process. Historically, gas flaring disposed of excess combustible gases or relieved the gas pressure within a system. There were no significant concerns about the environmental impact of emissions, and governmental agencies gave no incentives to maximize or recycle the gas destroyed in the flaring process.
Today, there is a shift from burning gas to reducing the amount released into the atmosphere. Natural gas is a valuable resource, and efforts to capture and recycle it into renewable energy take precedence over destroying it. Additionally, increasing pressure from global organizations and federal and state legislation encourages reducing emissions, and flare reduction is an effective method to achieve the desired goal. Recycling the waste gas minimizes the CO2 footprint and provides a source of onsite energy.
Today, gas flares are subject to stringent regulations, frequently requiring operators to measure, record, and report the amount of flared gases. Aside from measuring the flared gases, monitoring flare flow at various points within a complex run of pipes, including the actual flare stack, is often necessary. Flow monitoring gives the user an understanding of the gas source flowing to the flare and a relative flow rate.
Typically, gas flows to the flare system during the following:
- Operational upsets, interruptions, or emergencies when process equipment must be quickly depressurized to avoid equipment damage
- Start-up or shutdown, when the gases cannot be safely channeled back to the system’s storage or process. Venting gas may also be required for maintenance or regeneration.
- Continuous flare operation may include uninterrupted sweep gas through the piping systems to maintain positive pressure and prevent the buildup of combustible gases. It is also typical to provide process venting of equipment such as analyzers, gas seals, and pressure control. Additionally, pressure relief valve leakage is commonly flared.
Flow Meter Challenges
There are inherent challenges for operation or measurement engineers within many flare gas applications to select the proper flow meter. When choosing the appropriate instrument, consider the following:
Mixed Gases and Calibration – Thermal mass flow meters (TMFMs) measure heat transfer and relate heat transfer to mass flow based on the calibration. Since various gases have different heat transfer properties, the thermal mass flow meter (TMFM) must be calibrated with the specified gas to measure the flow rate accurately. Sage Metering (SAGE) calibrates its flow meters using the actual gas mixture (or a mixture close to the specified composition). This calibration method is more accurate than using air with correction factors for different gases, another commonly used calibration practice.
Whenever there is a mixture of gases, the composition is unlikely to remain consistent. Variations in gas mixture often occur on a seasonal basis. If known, SAGE can predict the variations in performance based on the different gas compositions.
Wide Turndown Ratio Required – It is critically important that the instrument can measure extremely low flow associated with normal venting conditions while simultaneously accurately measuring extremely high flow during an emergency or upset situation.
Environmental Regulations – Flow meters must meet accuracy and calibration requirements established by the EPA and emissions trading regulations. Some ecological agencies and emissions trading regulations require flow meters to be accurate to ±5% or better, as referenced in 40 CFR 98.3.
Hazardous Location – Because gas is combustible and flammable, the flow meter must be approved for use in a hazardous location by the appropriate agency. The approval should not rely on an enclosure-only classification but on the entire flow meter.
Pipe Access Limited – Access to areas where flow meters must be installed, serviced, and maintained can be challenging in flare gas applications. Ultrasonic spool-type meters typically require lengthy shutdown time and high labor costs to install and maintain these meters.
Large Pipes – Effective flow meter options reduce as pipe sizes are increased.
Limited Straight Run – Some facilities, such as offshore platforms, have limited space; obtaining sufficient straight runs to attain repeatable flow precision can be difficult.
Changes in Gas Composition and Hydrogen
When selecting flow meters for flare gas applications, other unique challenges for engineering involve changes in gas composition and the presence of hydrogen.
Gas Composition Impact
The most significant issue with measuring gas flow using a TMFM (flare gas flow meter) is the change in gas composition. This is not as much of a concern when measuring biogas, landfill, and natural gas. These gases may have minor changes in overall gas composition, but the impact is insignificant. Conversely, gas composition variation at refinery and chemical plant applications can significantly influence flare gas flow measurement, resulting in unpredictable performance.
Hydrogen Impact
A small amount of hydrogen within the flare mix can generate inaccurate results using TMFMs. A TMFM measures heat transfer caused by gases as they flow past a heated sensor, and gases have different heat transfer characteristics. Hydrogen (H2) has a high thermal conductivity combined with low density, which gives it a significantly higher cooling capacity than other gases. Therefore, a small amount of hydrogen can create a high level of heat transfer, resulting in a higher measurement of the gas flow.
Typically, a main flare gas line (at refineries and chemical plants) contains a mixture of gases depending on where the gas comes from in the facility or unit. At times, the gases have a relatively constant composition; however, there can be significant variations. This can be further complicated when hydrogen is in the formation or there are changes in hydrogen content. Additionally, greater accuracy is required when reporting environmental emissions or determining a mass balance. All flow meters are affected by variations in gas composition; however, it is possible that SAGE can determine changes in accuracy by knowing the gas composition.
For this reason, in petroleum refineries or chemical plants with varying gas compositions, TMFMs are not traditionally suitable for accurate emission measurement or obtaining a mass balance for the main flare header. TMFMs (flare gas meters) can be used in branches or feed lines in these facilities to detect which operation or unit is sending flow to the flare.
New Sage Metering Engineering Approach
By knowing the gas composition, even in refineries and chemical plants, SAGE can predict accuracy with knowledge of the typical base gas composition and the variation in gas composition. SAGE has developed a method for modeling the heat transfer characteristics of a gas mixture. By analyzing the variations in gas composition, SAGE can use this model to predict variations in accuracy caused by deviations in gas composition. Due to the complexity of the convective heat transfer analysis, this determination of changes in convective heat transfer caused by varying gas composition cannot currently be done in real time, thus requiring analysis by SAGE engineers.
Flare Flow Measurement
EPA 40 CFR part 98
There are many operations or applications where waste gas is flared into the atmosphere. Flare stacks are typically seen at oil and gas wells, refineries, well-drilling rigs, natural gas plants, wastewater treatment plants, chemical plants, and landfills. Strict regulations, like the Mandatory Reporting of Greenhouse Gases Rule (40 CFR 98), require operations to measure, record, and report the amount of gas emitted into the atmosphere. EPA 40 CFR part 98 requires reporting by 41 industrial categories. The categories are further divided into subparts. For more information on EPA 40 CFR 98 and its subparts, refer to the SAGE white paper “Greenhouse Gas Emissions Monitoring Using Thermal Mass Flow Meters.”
European Union Emissions Trading Scheme
The European Union’s Emissions Trading Scheme (EU ETS) aims to reduce air pollution through economic incentives, specifically by trading greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions allowances. The program began in 2005 and covered facilities in 30 countries. Each country is given a cap on total emissions allowed in this scheme. Each facility in the program must measure and report its emissions yearly and surrender one allowance for every metric ton of CO2 or the equivalent amount of nitrous oxide (N2O) and perfluorocarbons (PFCs) they emit. If the facility emits less than its allowance, it can sell its credits; otherwise, it may buy credits from other installations. We are currently in the fourth phase, which has a trading period from 2021 to 2030.
Measurement
When flaring applications of known gas composition exist and water vapor isn’t condensing, TMFMs offer an attractive solution for flare gas metering. The SAGE meter has wide turndown, up to 1000:1 rangeability, accommodating extreme flow conditions and large flow swings. Under typical venting situations, low velocities are associated with flare gas, yet high velocities are typical in upset conditions. Additionally, their fast response to flow changes, low-pressure loss, accuracy (1% of reading plus 0.5% of full scale over a 100 to 1 turndown), and reproducibility make the meter a contender to ultrasonic flow meters in flare applications.
Companies are taking advantage of the installed cost savings associated with TMFMs, which are $5,000 or less versus $50,000 or more for an ultrasonic application. While a bit more inconvenient than an ultrasonic meter, in many cases, the savings warrant the inconvenience. Operators realize that by identifying the gas at the flare application, SAGE can adjust the meter to measure the known flare gas. This works for applications where compositional changes are known or are seasonal.
SAGE Insertion Style TMFMs provide the wide turndown required to cover the extremely low flows (low velocities) associated with standard venting and the extremely high flow (high velocities) associated with an upset condition. Their fast response to flow changes, low-pressure drop, and reproducibility are important characteristics of a flare application.
In-Situ Calibration Verification
In addition, SAGE products provide the customer with a unique in-situ calibration check at a “no-flow” (0 SCFM) condition. This important procedure ensures that the meter has retained the original NIST Traceable Calibration, verifies the meter’s accuracy, confirms that the sensors are clean, and ensures that the flow meter hasn’t drifted or shifted. This is a tremendous benefit since it eliminates the cost and inconvenience of annual calibrations on the flow meter and provides the data needed to comply with many environmental protocols.
Applications
Biogas and Landfill Gas

Biogas, digester gas, and landfill gas can be produced from industrial wastewater treatment, farming operations, municipal solid waste landfills, and industrial waste landfills. These gases contain a mixture of methane (CH4), carbon dioxide (CO2), and minor quantities of other constituents. The gases can also be converted to renewable energy and fuel onsite boilers, with the excess gas being flared. They can also generate electricity, sell the energy to local industries, or even create fuel for natural gas-fueled vehicles.
If the operator is allowed to, they may release the flammable gas directly into the atmosphere or burn it with a flare. With a focus on reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, flaring the gas provides an opportunity to lower emissions. Biogas from a digester is a mixture of approximately 65% CH4 and 35% CO2, while landfill gas is closer to half CH4 and CO2. This gas can then be captured and destroyed in a process called methane destruction, which is accomplished by flaring the gas. While the process creates carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, it destroys methane, which is 21 times more potent than CO2. For this reason, flaring biogas, digester gas, and landfill gas are viable methods to lower GHG emissions.
Natural Gas Production
Whether natural gas production wells are on land or offshore, a flare is always either at or near the wellhead. Once a well has been drilled for gas, the well is tested to determine flow rates, pressure, and commercial viability. The natural gas is flared during the testing and until the well is functioning under regular operation. At the same time, the infrastructure is put in place to collect and transmit the natural gas to downstream processing. The gas may also be flared during regular operation if the gas pipeline is over-pressurized. Additionally, flaring the gas would be appropriate when maintenance is required at the well.
If natural gas wells are not located near a pipeline, it may be easier to flare off the gas. Similarly, if the amount of gas at a well is not deemed sufficient enough to justify the expense of building a pipeline, the gas may also be flared.
Natural Gas Processing Plants
Natural gas processing is the complex process of cleaning raw natural gas to eliminate impurities, non-methane hydrocarbons, and fluids. It begins at the wellhead and often involves the separation of oil and water from natural gas. Natural gas processing plants produce pipeline-quality natural gas. A natural gas processing plant may have a flare system with multiple branch lines connecting secondary process units to the main flare header. The waste gas would be recycled throughout this system through a vapor recovery system where the gas is recovered and returned to the process operation.
Natural Gas Pipelines
Natural gas pipelines route natural gas across long distances to and from compressors and distribution centers. Flares may be found at compressor stations to flare the gas from pressure relief or blow-down valves. Additionally, gas leakage from compressor seals may also be flared or vented.
Offshore Platforms
On offshore production platforms, when natural gas is a byproduct, and the gas cannot be recovered or disposed of in any other manner, the gas is flared or burnt off. Flaring natural gas can be measured with the SAGE TMFM, which has a unique wide turndown by taking extra data points during calibration.
30 CFR Part 250 Subpart K
Federal Regulation Title 30 CFR Part 250 Subpart K Oil and Gas Requirements require operators to meter flare and vent gas volumes for deepwater facilities processing more than an average of 2000 barrels per day during a calendar month. As stated by 30 CFR 250.1163 (a) (2), “The flare/vent meters must measure all flared and vented gas within 5 percent accuracy.”
Crude Oil Extraction
Natural gas is commonly produced during petroleum crude oil extraction. When oil is pumped from the ground, it typically contains water and natural gas. For oil and natural gas to be considered pipeline quality, they must be separated by a separator. Here, the gas is removed and sent to a separate pipeline while the remaining oil and water are heated and treated, separating the oil and water. Residual natural gas or hydrocarbons are generally vented to the atmosphere or processed further while the oil goes to storage tanks. The vented vapors typically have a low flow within small pipes (4”). Alternatively, when oil wells lack the infrastructure required to recover the natural gas, typically because the wells are in remote locations, much of the associated gas is flared as waste gas.
Oil Refineries and Chemical Plants
The facility may have a flare system with multiple branch lines connecting secondary process units to the main flare header at refineries. The waste gas would be recycled throughout this system through a vapor recovery system where the gas is recovered and returned to the process operation. As previously indicated, TMFMs are not traditionally suitable for accurate emission measurement or obtaining a mass balance for the main flare header due to the extreme variations in gas composition. TMFMs can be used in refineries or chemical plants to detect which specific operation sends the gas flow to the flare.
Oil Refinery Regulations: EPA 40 CFR Part 60 Subpart Ja
EPA 40 CFR Part 60 Subpart Ja are performance standards for petroleum refineries, including flare flow measurement. The regulations require that all flares, except for emergency flares, be continuously monitored for gas discharge to the flare. The thrust of this regulation is that the EPA encourages refineries to install flare gas recovery systems which will “reduce emissions of SO2 by 3,200 tons/year, NOx by 1,100 tons/year, VOC by 3,400 tons/year and CO2 by 1,900,000 metric tons/year from the baseline.” 1 While these regulations apply to refineries only, the oil and gas industry considers this a possible future standard. As previously indicated, TMFMs are unsuitable for this application due to the potential for significant modifications in the gas composition.
Atmospheric Storage Tank Vent
Atmospheric storage tanks are large aboveground containers commonly used in oil and gas production, containing oil or gas condensate liquids. Storage tank emissions from venting are primarily volatile organic compounds (VOC) and considered hazardous air pollutants (HAP). Regulatory agencies may require that the emissions be quantified and reported. Additionally, reporting tank venting for greenhouse gas emissions is required under 40 CFR part 98.
Direct measurement of the vented vapors using TMFMs provides an accurate emission quantification method. Emissions are generated from flashing, working losses, and breathing losses:
- Flash gas is created when a gas or liquid stream experiences a pressure drop or a temperature increase. Flash tank emissions can occur at compressor stations, gas plants, pigged pipelines, tank batteries, or the wellhead.
- Working losses are emissions that result from the change in liquid level within the tank. As the tank is filled, the vapors within the tank are displaced and flow out of the vent. Typical locations include the wellhead, storage tanks, and liquid loading and unloading facilities.
- Breathing losses occur when vapors are discharged from a tank due to pressure or temperature changes. They also include vapors from the evaporation of the liquid in the tank.
Mass Flow Measurement
Flow Measurement Technologies
Ultrasonic Flow Meters
Measuring flare gas becomes a challenge for most flow meters. Ultrasonic Flow Meters are very accurate and effective tools for measuring flare gas. They tolerate some condensed liquid, are not affected by gas composition, and endure fluctuations in pressure and temperature. However, with this type of performance come high costs ranging from $50,000-$100,000 per installation. The ultrasonic meter does require pressure and temperature measurements to obtain mass flow.
Ultrasonic flow meters measure the difference in transit time of pulses that travel from a downstream transducer to the upstream transducer compared to the time from the upstream transducer back to the downstream transducer. They can also determine a gas’s molecular weight by measuring the speed of sound. The flow meter then uses this data to get a mass flow measurement in real time when variations in gas composition occur.
Averaging Pitot Tube
Averaging Pitot Tube is a differential pressure flow measurement device. The instrument has limitations with gas flow measurement, especially low flow sensitivity, and has limited turndown. The measurement is contingent upon achieving velocity pressure. There may be insufficient velocity at low flow rates to obtain a suitable signal. Additionally, if there are changes in the specific gravity of the gas, the pressure drop is impacted, creating a flow measurement error.
Thermal Mass Flow Meters
Thermal mass flow meters are suitable for measuring flare gas when the gas composition is consistent and known, and there is no condensation. Additionally, when the operator is willing to trade off lower accuracy in some applications, the TMFM can save money versus the expense of an ultrasonic flow meter.
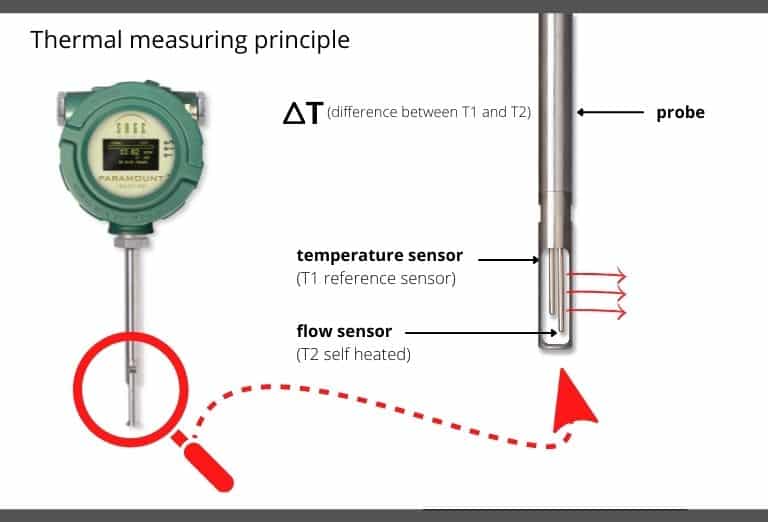
Principals of Thermal Mass Flow Measurement
Thermal mass flow meters measure gas flow based on the principle of convective heat transfer. Either insertion-style probes or inline flow bodies support two sensors in contact with the gas. The sensors are resistance temperature detectors (RTDs). The SAGE sensors consist of highly stable reference-grade precision-matched platinum windings clad in a protective 316 SS sheath for industrial environments.
One of the sensors is heated by the circuitry and serves as the flow sensor, while a second RTD acts as a reference sensor and measures the gas temperature. The SAGE proprietary sensor drive circuitry maintains a constant overheating between the flow and reference sensors. As gas flows past the heated sensor (flow sensor), molecules of the flowing gas transport heat away from this sensor, the sensor cools, and energy is lost. The circuit equilibrium is disturbed, and the temperature difference (ΔT) between the heated and reference sensors has changed. The circuit will replace the lost energy within one second by heating the flow sensor to restore the desired overheat temperature.
The power required to maintain this overheat represents the mass flow signal. There is no need for external temperature or pressure devices.
One of the advantages of TMFMs is that they have no moving parts, which reduces maintenance and permits their use in difficult application areas. They also do not require temperature or pressure corrections to obtain mass flow and provide good overall accuracy and repeatability over a wide range of flow rates. This meter style measures mass flow rather than volume and is one of the few categories of meters that can measure flow in large pipes and ducts.
Sage Metering Difference
SAGE provides thermal mass flow meters that are factory calibrated and configured for the specified application, which makes installation easy. They can be installed directly into the pipe without needing field setup and calibration. SAGE offers insertion and inline TMFMs with built-in flow conditioners that monitor flow rates. These direct mass flow meters are highly accurate and repeatable and have negligible pressure drop.
The SAGE meter has extraordinary rangeability of at least 1000 to 1. Because of its low-end sensitivity and wide turndown, the SAGE TMFM can accurately measure extremely low velocity, down to 5 SFPM, making it highly effective for measuring the low flow rates associated with standard venting. Yet, it can also accurately measure the extremely high flows associated with upset conditions. In addition to the 4 – 20 mA control output, the meters provide pulsed consumption outputs and Modbus-compliant RS485 RTU communications. The meters feature bright graphical displays of flow rate, totalized flow, gas temperature, and continuous diagnostics. For difficult-to-reach pipes or locations with extreme radiant heat, SAGE also offers a remote-style flow meter with up to 1000 feet of lead-length compensated cable – all electronics and powering are done at the transmitter – thus, the probe or flow body has a terminal junction box.
Calibration Verification
The SAGE TMFM comes from the factory fully calibrated and can easily verify that it maintains its original factory calibration through an in-situ calibration verification.
All SAGE Paramount and Prime meters can perform the in-situ calibration check as long as a “no-flow” (0 SCFM) condition can be created. “No flow” is easily created using an isolation valve assembly with the insertion meter style. Unlike other TMFMs, the SAGE In-Situ Calibration verifies that the unit is accurate and indicates that the sensor is clean. If the meter does not pass the calibration check the first time, in most cases, simply cleaning the sensor and re-testing will verify that the meter is accurate and hasn’t drifted or shifted.
Hazardous location

The SAGE Prime® is in a dual-sided NEMA 4 enclosure with easy access to a separate rear compartment. The Prime is CE compliant and meets Class 1, Division 2 standards for hazardous service.
The Sage Paramount has an explosion-proof NEMA 4X enclosure with standard Cl I Div 2 and optional Cl I Div 1 approval (Groups B, C, D, T4).
Summary
Flaring and venting systems are used globally to burn off waste gas and surplus gases. They are also a safety means to protect equipment, the system’s processes, and the environment. Flaring systems are used extensively in natural gas drilling, production, transmission, oil drilling, refineries, chemical processing plants, wastewater treatment, landfills, and farming operations.
The extraordinary rangeability and ease of installation of SAGE Thermal Mass Flow Meters offer economical solutions for the measuring, monitoring, and reporting of flare gas in various systems, including biogas, landfill gas, and natural gas, as well as applications at oil refineries and chemical plants when the gas composition is known.
In addition, in cases of variable composition, SAGE can provide an error analysis, which, if acceptable to the operator, may offer an alternative to the expense of ultrasonic flow meters.
We welcome the opportunity to review your application and recommend the best solution to achieve your objective.
[1] Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and RTI International (2012). Regulatory Impact Analysis: Petroleum Refineries New Source Performance Standards Ja. 65.