Natural Gas Distribution (Non-Custody Transfer Applications)
A thermal mass flow meter is ideal for natural gas distribution measurement in non-custody transfer applications, such as natural gas flow monitoring. They also can be used to help avoid pipeline bottlenecks and future planning, by measuring real-time usage throughout the year.
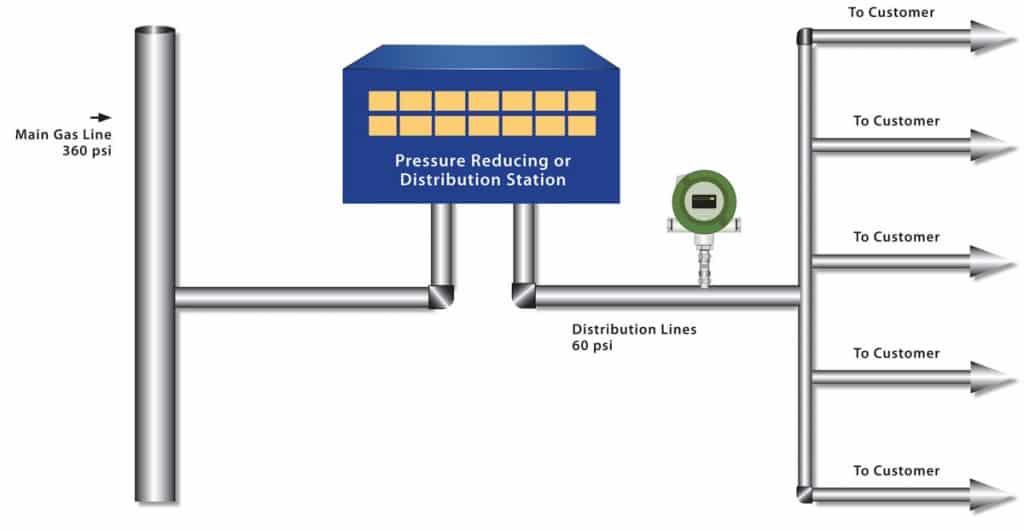
Natural Gas Distribution

Natural gas distribution companies measure their customers’ total gas usage during a specific time period through their custody transfer flow meters. What these meters fail to communicate is the actual usage at various distribution points in the many feeder lines.
Distribution Pipelines
Distribution pipes, or “mains,” are the intermediate phase between high-pressure transmission lines and low-pressure service pipelines. They operate at an intermediate pressure, varying from 30 psi up to 450 psi within small to mid-sized pipes, ranging from 2” to 24”. The distribution pipes may be steel, cast iron, polyethylene (plastic), or occasionally copper.
Service Lines
The service pipelines are metered and deliver natural gas to the ultimate gas customers. They are small pipes, typically polyethylene, steel, or copper, ranging from ½” to 2″ and transmit the gas at low pressures ranging from 6 to 10 psi.
Real-Time Non-Custody Applications to Avoid Bottlenecks

To ascertain gas usage in distribution systems, flow meters can be installed to provide real-time measurements at different locations. Peak gas consumption periods are in the morning and early evening, with less during the middle of the day and night. Gas consumption also varies during the year with peak usage for heating during winter months. Some gas distribution companies use meters at the intermediate line to balance and model their system.
A thermal mass flow meter is ideal for these applications because of their direct mass flow measurement, high rangeability, and simplicity of installation by inserting the probe into the pipe through a ball valve and compression seal.
Gas distribution companies can better ascertain consumption requirements to help avoid pipeline bottlenecks and future planning, by measuring real-time usage throughout the year.
Natural Gas Flow Monitoring
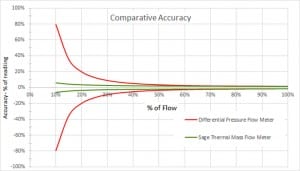
Many natural gas distribution companies use differential pressure flow meters upstream of custody transfer meters to monitor the gas flow to multiple industrial customers. Unfortunately, gas flow can vary considerably depending on the time of the year, and differential pressure flow meters have poor accuracy at low flow conditions. For this reason, thermal mass flow meters can more accurately measure natural gas flow at these low flow rates. Rangeability of thermal mass meters can be as high as 100:1.
Considerations for Flow Meter Selection

- Mass flow measurement without the need for temperature and pressure correction Easy in-situ calibration verification method to verify the accuracy and operation of the sensor and transmitter
- Wide turndown for precision measurement at low or high flow
- With varying gas pressures and flow rates, the thermal mass meter has excellent low flow sensitivity and negligible pressure drop
- Easy installation
- Approved for use in hazardous area
- Calibrated for natural gas composition
- Probe retraction device for easy removal for cleaning
Recommended Sage Models for this application
- Sage Prime
- Sage Paramount