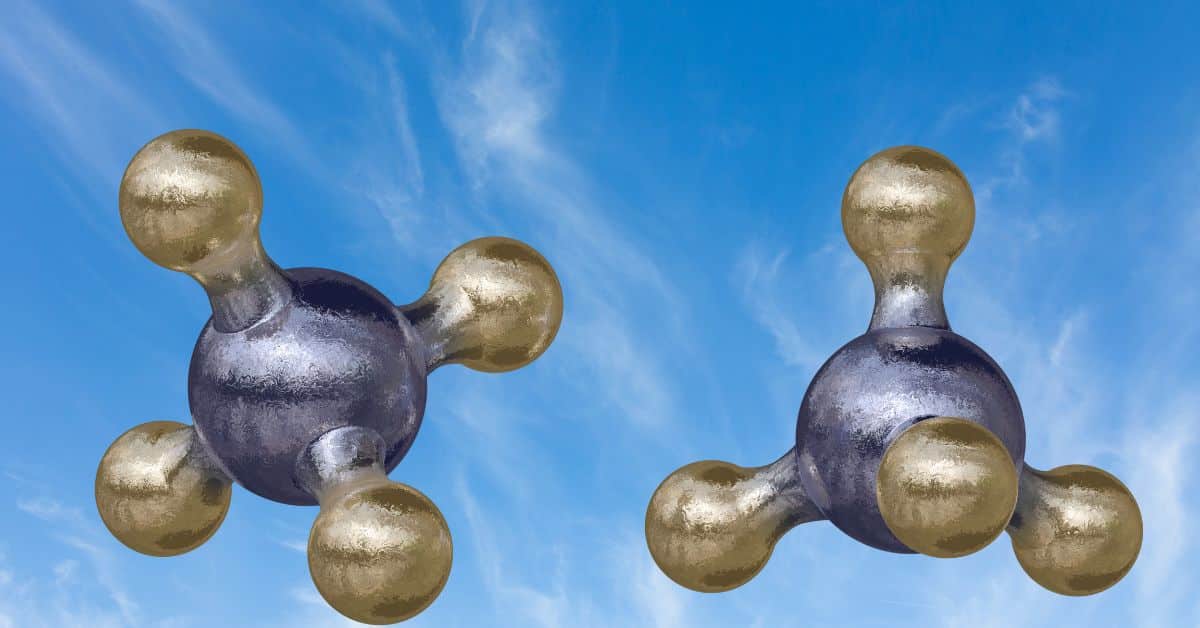
Ammonia
In industrial manufacturing, ammonia is used to produce fertilizer, is an industrial coolant, and reduces NOx emissions from combustion sources. In all these areas, ammonia gas met…
Argon
Argon is a noble or inert gas with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is odorless, colorless, monatomic, and unreactive toward other elements. It is the third-most abundant gas…
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a central heat-trapping gas, or greenhouse gas, that comes from the gathering, producing, and burning of fossil fuels (such as coal, oil, and natural gas),…
Biogas, Biomethane, or Renewable Natural Gas (RNG)
Biomethane is a renewable natural gas (RNG) that is produced from biogas or decaying organic matter, such as sludge from wastewater treatment, food waste, animal manures, landfill…
Ethanol
Ethanol is an organic compound, an alcohol with the chemical formula C₂H₆O. Its formula can also be CH₃−CH₂−OH or C₂H₅OH. Ethanol is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a…
Helium
Helium is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas with the tee symbol He and atomic number 2. It is the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table…
Hydrogen
At standard conditions, hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula H₂ and is the lightest element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. It is colorless, odorless,…
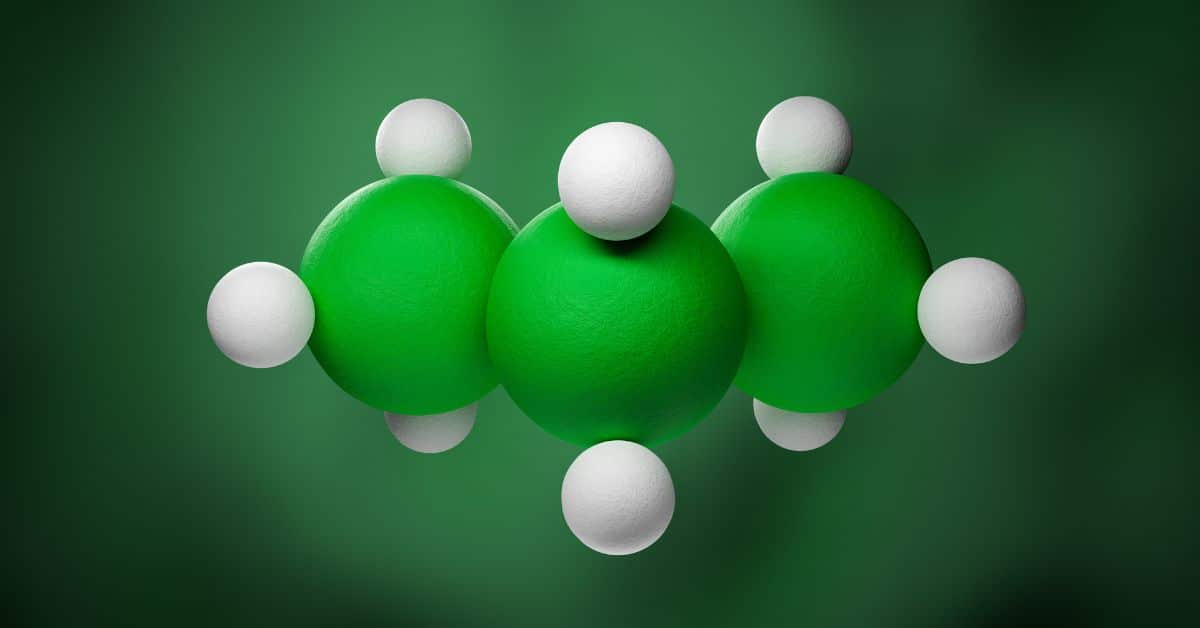
Methane
Methane (CH4) is a powerful greenhouse gas found in small quantities in the atmosphere. Methane is the simplest hydrocarbon, consisting of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms….
Nitrogen Gas
Nitrogen (N2 gas) is an inert gas used in various applications, including cutting, purging, cooling, and freezing, and nitrogen gas flow meters are required in: Food processing Ste…
Oxygen
Oxygen is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, a…
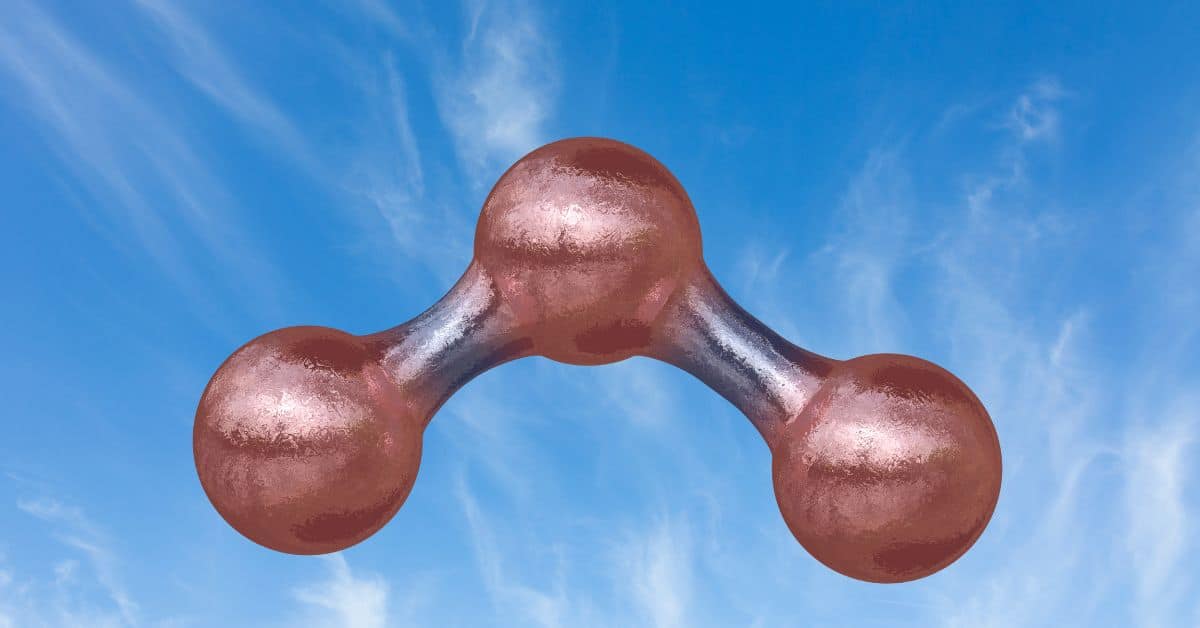
Ozone
Ozone is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is inorganic with the chemical formula O₃ and an allotrope of oxygen, which is much less stable than the diatomic al…
Propane
Propane is a gas at standard temperature and pressure but is compressible to a transportable liquid. It is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula C₃H₈. How can we help yo…
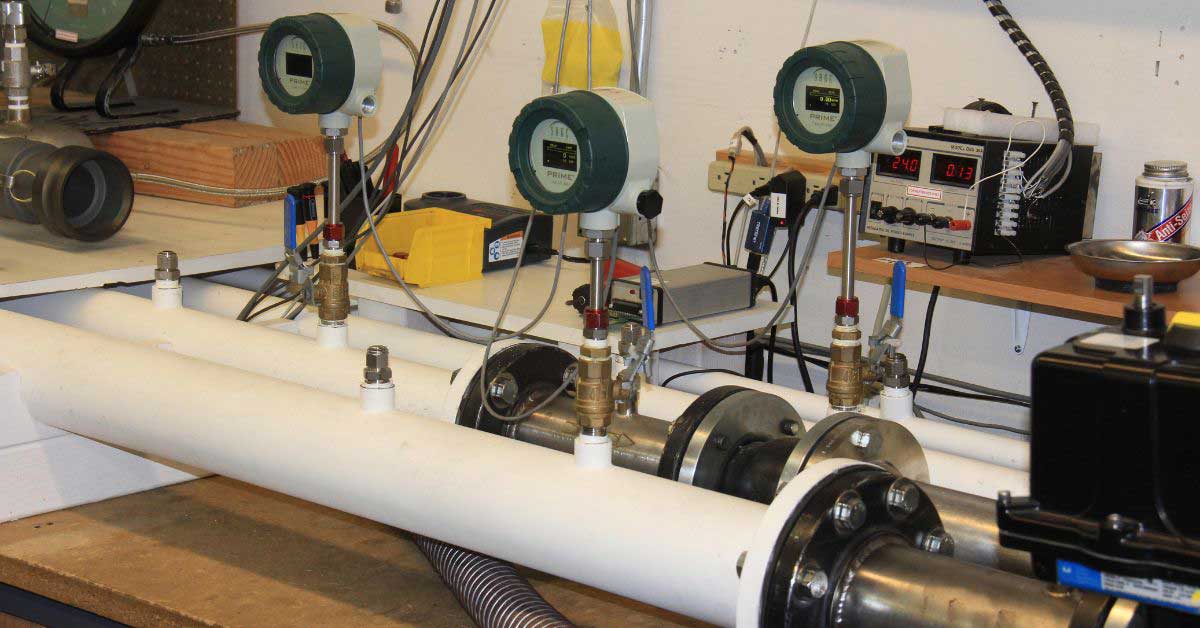
Thermal Mass Flow Meter Calibration
A thermal mass flow meter calibration is the foundation for accurate gas mass flow measurements. Without calibration, the meter readings are suspect. The flow meters are calibrated…
Air Separation Gases
Air separation plants separate atmospheric air into its primary constituents, which are approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 0.9% Argon and a handful of rare inert gases (xenon,…
Natural Gas Flow Measurement
Natural Gas Application Guide Natural gas measurement is where Sage thermal mass flow meters excel. There are various applications where the natural gas flow rate is needed, partic…
Flue Gas
Flue gas measurement is often required for environmental reporting, and thermal mass flow meters offer a reliable means to measure and monitor flue gases which contain greenhouse g…
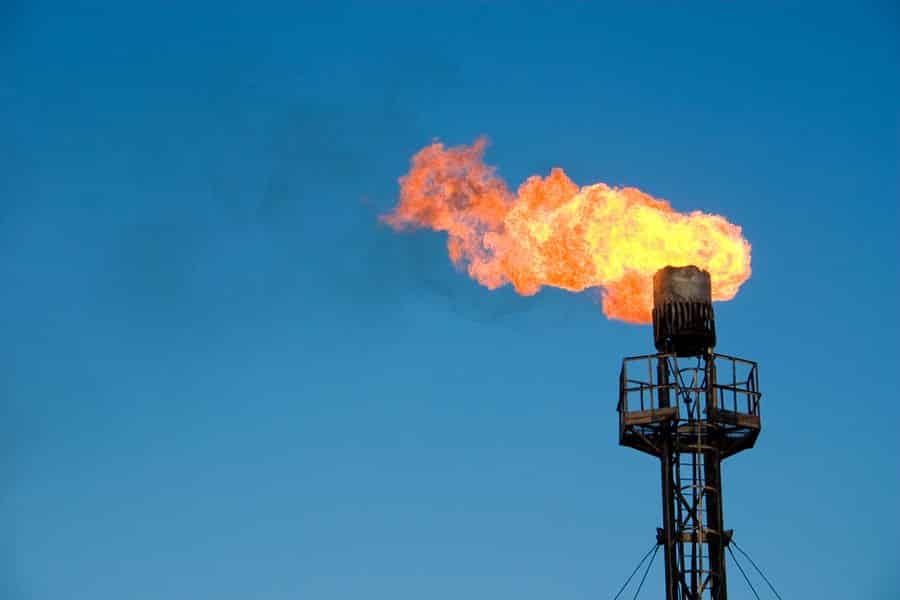
Flare Gas
Oil Refineries, well drilling operations (such as offshore oil rigs), wastewater treatment plants, chemical processing plants, natural gas plants, and landfills are but a sampling…
Combustion Air Flow
Natural Gas Application Guide One of the most important ways to reduce energy consumption in a manufacturing environment is to optimize the combustion control on industrial boilers…